The theoretical subjects in ATPL certification cover a wide range of essential knowledge areas required for the safe and efficient operation of commercial aircraft. These subjects include aviation law, aircraft general knowledge, instrumentation, mass and balance, performance, flight planning, human performance, meteorology, navigation, operational procedures, principles of flight, and both VFR and IFR communications. Additionally, Area 100 KSA focuses on critical thinking, teamwork, and decision-making under pressure.
Pilots must pass individual exams for each subject, with varying time limits depending on the complexity of the topic. These exams ensure that pilots have a deep understanding of flight operations, aircraft systems, and navigation, preparing them for real-world scenarios as they progress toward becoming captains.


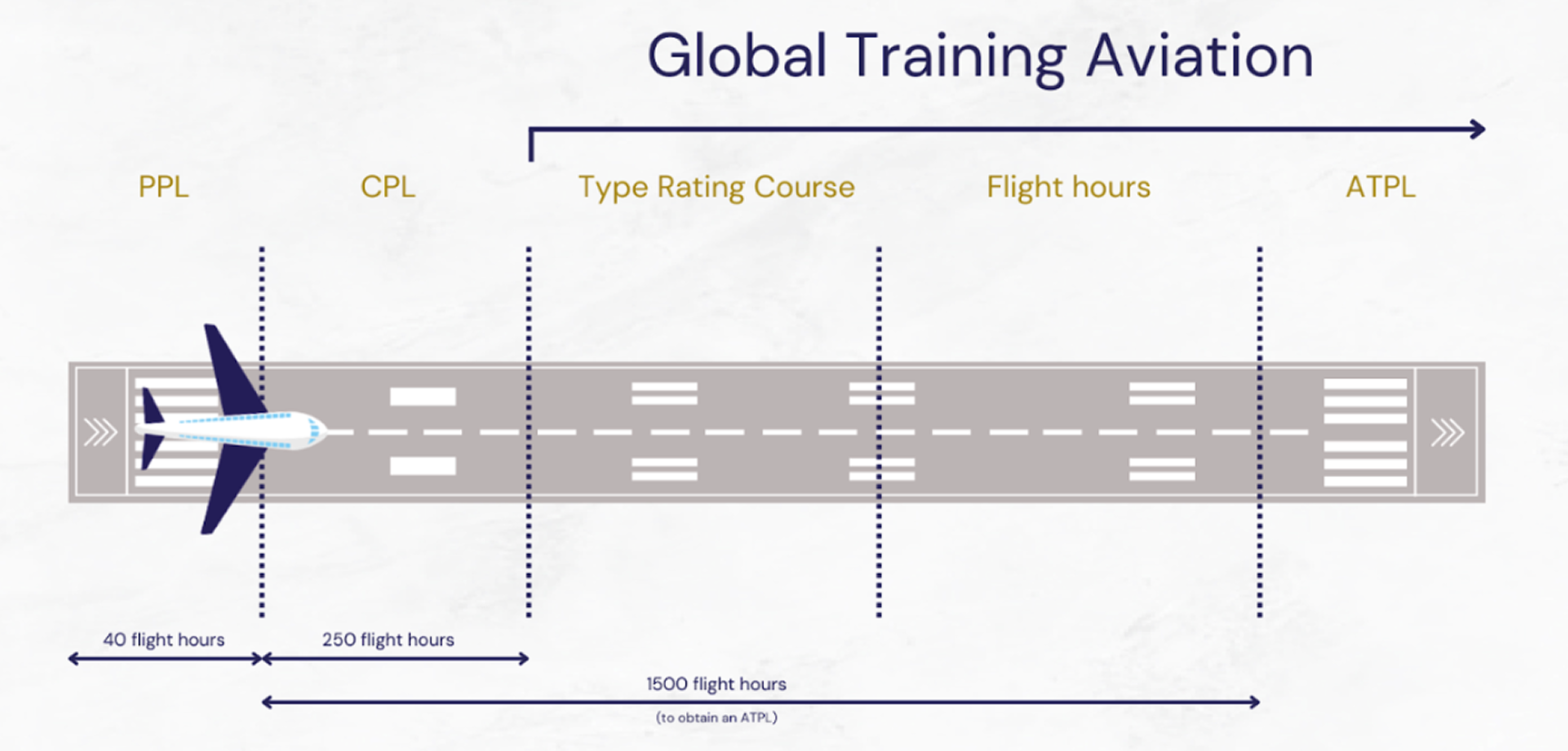
The ATPL (Airline Transport Pilot License) and the CPL (Commercial Pilot License) are both essential for pilots, but they serve different purposes and come with different levels of responsibility.
The ATPL is a higher-level license, often considered more advanced than the CPL, as it is designed for pilots who wish to operate as captains in commercial aviation. The ATPL includes comprehensive training in both theoretical knowledge and practical skills, preparing pilots for the demands of flying large commercial aircraft in complex airline operations. It is required for those seeking to operate in the cockpit of an airliner as a captain.
On the other hand, the CPL allows pilots to work as commercial pilots, but it is typically a stepping stone toward obtaining the ATPL. With a CPL, pilots can be employed in commercial aviation, but they are usually qualified to work as first officers or co-pilots, not as captains. The CPL involves a less extensive theoretical curriculum compared to the ATPL, focusing on the essential skills for flight operations.
In terms of which is “better,” it depends on the pilot’s career goals. If the aim is to become a captain in commercial aviation, the ATPL is the ultimate goal, as it is required for higher-level positions and offers more opportunities. However, the CPL is the foundation from which pilots typically build up their experience and qualifications before progressing to the ATPL.
Yes, an ATPL is required to be a captain in commercial aviation. While a CPL allows you to work as a first officer, only the ATPL qualifies you to command an airliner, as it proves you have the advanced skills and knowledge needed for the role.
Yes, obtaining an ATPL can be challenging. It requires extensive theoretical knowledge, practical flight experience, and the successful completion of exams and assessments. Pilots must accumulate numerous flight hours, undergo simulator training, and demonstrate advanced skills in various aspects of aviation. The process is demanding, but it is essential for those aiming to become captains in commercial aviation.
The main difference between integrated ATPL and modular ATPL lies in the structure and approach to training.
An integrated ATPL is a structured, full-time program that combines all the required training elements into a single, continuous course. It typically starts from the beginning, taking students through the entire process from private pilot to ATPL, with a clear, set timeline. This approach is more intense but ensures that the training is streamlined and comprehensive.
In contrast, a modular ATPL allows for more flexibility. Pilots can complete different parts of the training at their own pace, often starting with a private pilot license (PPL) and progressing through each stage separately. Each module is completed independently, allowing pilots to spread out their training and potentially work in between modules. While this approach can be more flexible and affordable, it may take longer to complete.
In you want to know more about these differences, click here to read this article.